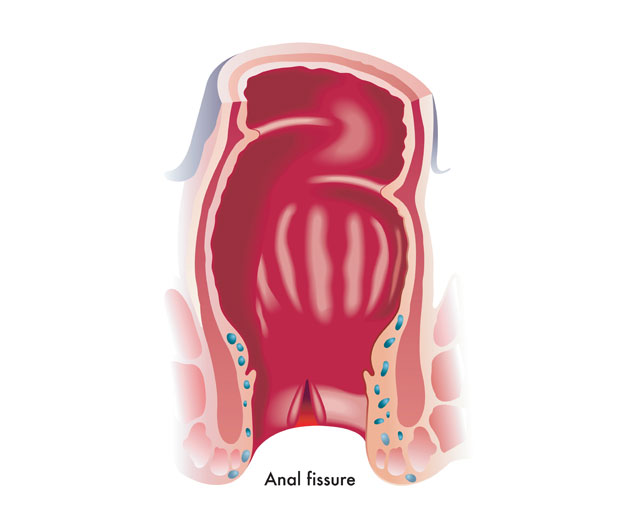
Anal fissures are a common and painful medical condition that affects the anal canal. Characterized by small tears or cracks in the lining of the lower rectum, these fissures can lead to extremely painful bowel movements and bleeding that greatly impact one's quality of life.
While it is not life-threatening, anal fissures can be very distressing and challenging to manage without proper care. Fortunately, with the help of a colorectal doctor, patients can receive personalised and effective care to resolve the issue.
What Causes Anal Fissures?
Possible causes of anal fissures include:
- Chronic constipation and straining during bowel movements
- Passing large or hard stools
- Diarrhoea
- Crohn’s disease
- Anal injuries
- Childbirth
- Rectal cancer
What are the Signs & Symptoms of Anal Fissures?
- Sharp pain during and after bowel movements
- Bright red blood from the anus
- Blood on toilet paper and/or on stools
- Skin tag around the anus (in chronic cases)
How are Anal Fissures Diagnosed?
They can be diagnosed through an evaluation of the patient’s medical history, such as symptoms experienced, when they started, how often, one’s lifestyle and dietary habits, as well as anything that seems to worsen or soothe the pain.
This is usually followed by a visual and/or physical examination (using an anoscope) by the colorectal doctor. If necessary, a digital rectal examination may also be performed, whereby the doctor will gently insert a lubricated, gloved finger into the rectum to assess the sphincter muscle and any other abnormalities.
It is important to get assessed for an accurate diagnosis as the symptoms of anal fissures can be similar to other more serious medical conditions such as certain infections or tumours.
How are Anal Fissures Treated?
The primary goal of anal fissure treatment is to regulate stool consistency, promote healing of the fissure, alleviate pain and bleeding, and reduce the chances of recurrence. This may include lifestyle and dietary changes, medical treatments and possibly surgical treatments, if deemed necessary.
- Dietary Changes: Making appropriate dietary changes is crucial to making stools softer. This includes increasing one’s fibre intake and eating more fruits, vegetables, and staying well-hydrated.
- Stool Softeners: The doctor may prescribe stool softeners to help prevent constipation and make it easier to pass stools more smoothly.
- Topical Medications: The doctor may prescribe topical creams or ointments that help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Sitz Baths: Warm sitz baths promotes pain relief by soothing the anal area and improve blood flow to the region, thereby speeding up the healing process.
- Using Moist Tissues: Using moist tissues or baby wipes to clean up oneself after a bowel movement may be a better and gentler option than rough, dry toilet paper.
- Muscle Relaxants: In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications that can relax the anal sphincter muscles in a bid to reduce spasms (which hinders healing).
- Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy: This involves cutting a small part of the anal sphincter muscle in order to relieve pressure, spasm and pain; and promote healing. Surgery is often the best option in the case of chronic fissures.
What is the Success Rate & Recovery of Treatment?
Most patients usually return to most of their daily activities few days following surgery. However, complete healing will take up to 6 to 10 weeks. The patient must adhere to good lifestyle and dietary habits to ensure that the chances of recurrence are minimised. A lateral internal sphincterotomy has a high success rate of over 90%; though it does come with a small risk of faecal incontinence. A colorectal surgeon will be able to advise you on the best possible treatment plan for your specific case.
Does Having Anal Fissures Increase the Risk of Cancer?
No, there is no relation to cancer – anal fissures do not cause cancer, nor do they increase the risk of it. However, certain serious conditions may present with similar symptoms as anal fissures. Hence, your doctor may recommend further tests even after an anal fissure has healed so as to rule out other possible causes of the rectal pain and bleeding.